QMS in Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide
How Continuous Improvement Drives Manufacturing Excellence
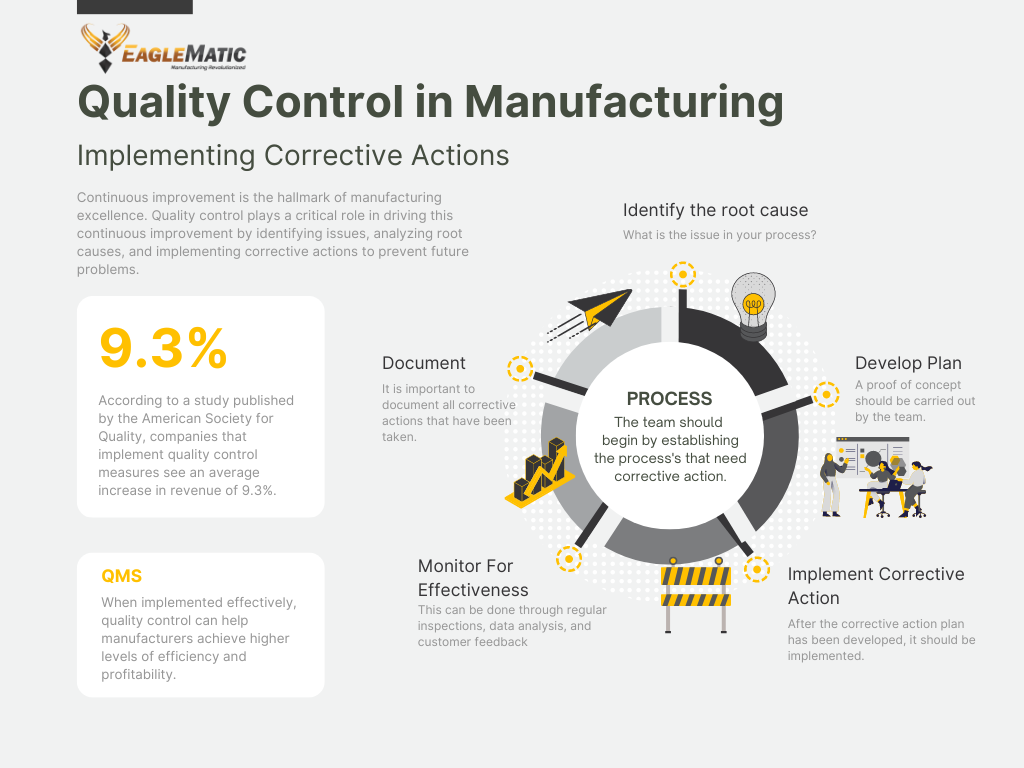
Continuous improvement is the hallmark of manufacturing excellence. Quality control plays a critical role in driving this continuous improvement by identifying issues, analyzing root causes, and implementing corrective actions to prevent future problems. When implemented effectively, quality control can help manufacturers achieve higher levels of efficiency, productivity, and profitability. In this article, we will explore how quality control drives manufacturing excellence through continuous improvement, and how manufacturers can implement effective quality control measures to achieve success in the industry. From identifying areas for improvement to implementing corrective actions, we will cover everything you need to know about using quality control to drive manufacturing excellence.
What is Quality Control?
Quality control in manufacturing refers to the process of ensuring that products meet or exceed the desired quality standards. It involves a series of checks and inspections throughout the manufacturing process to identify and eliminate defects, errors, or inconsistencies. Quality control measures may include product testing, statistical process control, visual inspections, and audits. The goal of quality control is to ensure that products are safe, reliable, and meet customer expectations. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also helps to minimize the cost of production by reducing waste and rework.
The process begins with defining quality standards and establishing a set of procedures to ensure that these standards are met. This may include establishing performance criteria, such as product specifications, tolerances, and requirements for functionality, safety, and durability.
Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control activities are carried out to ensure that products meet these standards. These activities can include:

- Raw material inspection: Ensuring that raw materials meet quality standards before they are used in the manufacturing process.
- In-process inspection: Monitoring the manufacturing process to identify and correct any defects or errors that may arise during production.
- Final inspection: A final inspection of finished products to ensure that they meet all required quality standards before they are shipped to customers.
- Testing and analysis: Conduct laboratory tests and analysis to verify that the product meets all performance criteria.
Key Principles of Quality Management in Manufacturing
Customer Focus: Quality management in manufacturing must start with a focus on the customer. Understanding customer needs and expectations are essential for producing products that meet those needs. Manufacturers must also ensure that their products comply with industry standards and regulations.
Continuous Improvement: Quality management is an ongoing process of continuous improvement. This involves regularly evaluating processes and procedures to identify areas for improvement and implementing changes to increase efficiency and product quality.
Employee Involvement: Quality management requires the involvement of all employees in the manufacturing process. This includes training employees on quality standards, providing feedback on product quality, and encouraging employee involvement in process improvement initiatives.
Data Analysis: Quality management involves the collection and analysis of data to monitor product quality and identify areas for improvement. This requires the use of quality control tools such as statistical process control (SPC), Pareto charts, and fishbone diagrams.
Supplier Management: Quality management in manufacturing also involves managing suppliers to ensure that they meet quality standards. This includes selecting suppliers based on their ability to meet quality requirements, monitoring supplier performance, and collaborating with suppliers to improve product quality.
The Importance of Quality Control in Manufacturing
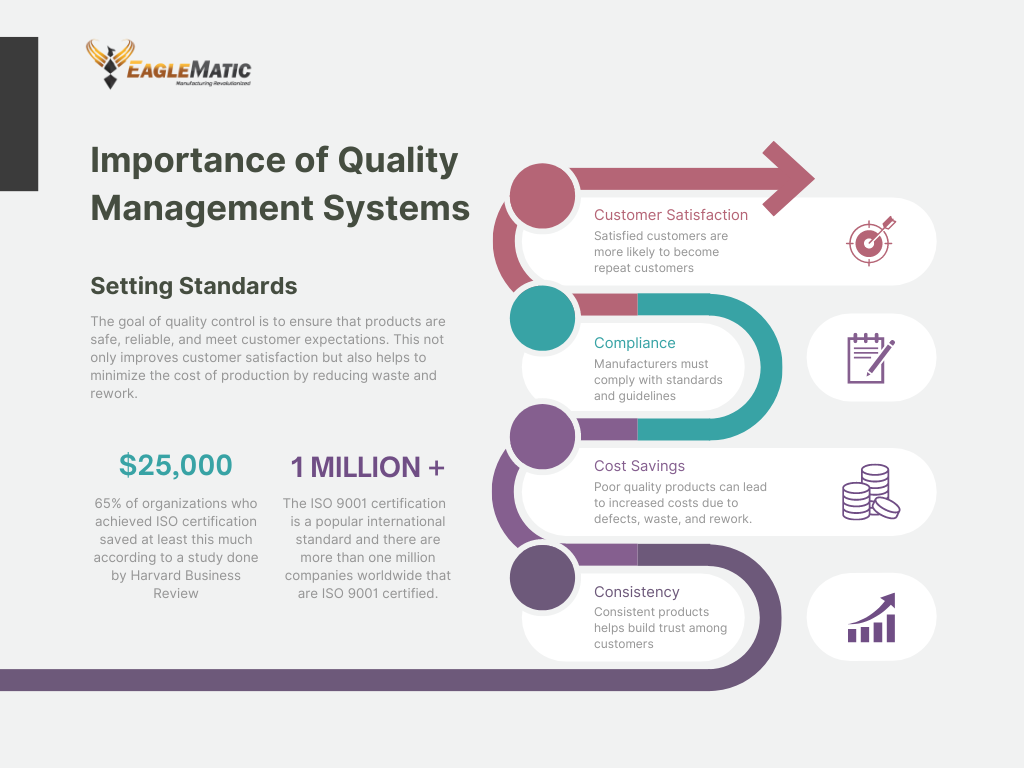
Quality control is essential in manufacturing for various reasons. It guarantees that products meet the quality standards set by the company. Meeting these standards is crucial as customers have expectations for the products they purchase. It also ensures that the products manufactured are safe and reliable. Unsafe and unreliable products can cause harm to customers and tarnish the reputation of the company. Implementing quality control measures can enhance customer satisfaction, which is crucial as satisfied customers are more likely to return to the company for future purchases and recommend it to others.
Here are some of the key reasons why quality control is important in manufacturing:
- Consistency: Quality control ensures consistency in the manufacturing process, which leads to consistent products. This helps build trust among customers and ensures that they receive products that meet their expectations every time.
- Cost savings: Poor quality products can lead to increased costs due to defects, waste, and rework. Quality control helps reduce these costs by identifying and correcting issues early in the production process.
- Customer satisfaction: Quality control ensures that products meet the desired quality standards, which leads to higher customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat customers and recommend the product to others.
- Compliance: Manufacturing companies must comply with various regulatory standards and guidelines to ensure that their products are safe for use. Quality control helps ensure that products meet these standards and regulations.
According to a study published by the American Society for Quality, companies that implement quality control measures see an average increase in revenue of 9.3%. This is because customers are willing to pay more for products that meet certain quality standards. Quality control also helps to reduce costs by minimizing waste and improving efficiency. According to another study, companies that implemented quality control measures saw a 20% reduction in defects and a 30% reduction in customer complaints.
How to Implement Quality Control in Manufacturing
To ensure that the manufactured products meet the desired quality standards, it is crucial to implement an effective quality control program. Here’s a detailed guide on how to implement quality control in manufacturing:

- Define the Quality Standards for each product
- Identify customer requirements: The first step is to identify the specific requirements and expectations of customers for the product. This can be done through market research, customer surveys, or by studying competitor products.
- Determine product specifications: Based on the customer requirements, determine the specifications of the product. This includes factors such as size, weight, material, performance, and other relevant characteristics.
- Set quality objectives: Based on the product specifications, set quality objectives that define the level of quality that needs to be achieved. Quality objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Determine acceptance criteria: Acceptance criteria define the level of quality that is acceptable for the product. This includes defining the tolerances and limits for each specification.
- Select a Quality Control Method
- Define quality characteristics: Define the quality characteristics that need to be measured, monitored, and controlled for the product or service. This includes identifying the critical quality parameters such as dimensions, color, texture, functionality, and other relevant attributes.
- Identify available quality control methods: Identify the available quality control methods that can be used to measure and control the quality characteristics of the product or service. The methods can include statistical process control (SPC), Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM), Lean Manufacturing, or other quality control methodologies.
- Evaluate the pros and cons: Evaluate the pros and cons of each quality control method based on its suitability, ease of implementation, and cost-effectiveness. This can be done through research, consultation with experts, or by conducting a pilot study.
- Train Employees for Quality Control
- Define training objectives: Clearly define the objectives and goals of the training program. This includes identifying the key competencies that the employees need to develop in order to perform their quality control responsibilities effectively.
- Develop training materials: Develop training materials that cover the key competencies and skills that employees need to learn. This can include presentations, videos, manuals, and hands-on training exercises.
- Use a variety of training methods: Use a variety of training methods to engage employees and help them learn more effectively. This can include classroom training, online training, on-the-job training, and coaching.
- Provide feedback and coaching: Provide employees with feedback and coaching to help them improve their skills and competencies. This includes regular performance reviews, coaching sessions, and recognition for good work.
- Reinforce learning: Reinforce learning by providing ongoing training and refresher courses to employees. This helps to ensure that their skills and competencies remain up-to-date and relevant.
- Create a Communication System for Reporting Defects
- Identify the reporting channels: Identify the reporting channels that will be used to report defects or potential issues. This can include a variety of channels such as email, phone, online forms, or a dedicated quality control hotline.
- Define the reporting criteria: Clearly define the criteria for reporting defects or potential issues. This includes identifying what constitutes a defect or potential issue and the severity levels for each.
- Develop reporting procedures: Develop procedures for reporting defects or potential issues. This includes defining the steps that employees need to follow when reporting an issue, the information that needs to be provided, and the deadlines for reporting.
- Establish reporting feedback: Establish feedback mechanisms to keep employees informed on the status of their reported defects or potential issues. This includes providing regular updates on the progress of the investigation and any corrective actions taken.
- Review and analyze reports: Review and analyze reports on a regular basis to identify trends and recurring issues. This information can be used to improve the QMS and prevent similar issues from occurring in the future.
- Create a Procedure for Handling Defects
- Identify the types of defects: Identify the types of defects that are likely to occur in the manufacturing process. This includes defining the criteria for what constitutes a defect and the severity levels for each.
- Define the roles and responsibilities: Define the roles and responsibilities for each employee involved in the defect handling process. This includes identifying who is responsible for reporting the defect, who is responsible for investigating and analyzing the defect, and who is responsible for taking corrective actions.
- Develop procedures for reporting defects: Develop procedures for reporting defects. This includes defining the channels for reporting defects, the information that needs to be provided, and the timelines for reporting.
- Develop a Procedure for Taking Corrective Action
- Identify the root cause: Identify the root cause of the problem using statistical methods such as Pareto charts, cause-and-effect diagrams (also known as fishbone diagrams), and control charts. Pareto charts help to identify the most common causes of defects, while cause-and-effect diagrams help to identify the underlying causes of the problem. Control charts help to identify trends and variations in the data over time.
- Develop a corrective action plan: Develop a corrective action plan that addresses the root cause of the problem. The plan should include specific actions to be taken to address the root cause, timelines for completion, and responsible parties.
- Implement the corrective action: Implement the corrective action plan and monitor its effectiveness using statistical process control methods such as control charts. This helps to determine if the corrective action is working and if additional actions are needed.
- Verify the effectiveness of the corrective action: Verify the effectiveness of the corrective action by monitoring the results and comparing them to the original problem. This helps to determine if the corrective action has been successful in addressing the root cause of the problem.
- Document the corrective action: Document the corrective action taken, including the root cause, the corrective action plan, and the results. This helps to ensure that the organization has a record of the actions taken and can use the information to improve its QMS in the future.
In addition to the above steps, there are various statistical methods that can be used to identify the root cause of a problem in QMS. These include Pareto analysis, fishbone diagrams, statistical process control, and Six Sigma methodologies. Each of these methods has its own strengths and weaknesses and should be selected based on the specific problem being addressed.
Pareto analysis is a method for identifying the most common causes of defects or problems by ranking them in order of frequency. Fishbone diagrams, also known as cause-and-effect diagrams, help to identify the underlying causes of a problem by organizing potential causes into categories. Statistical process control involves using statistical methods to monitor the production process and identify when a process is out of control. Six Sigma methodologies involve using statistical methods to improve quality and reduce defects.
By implementing these steps, you can ensure that your products meet the desired quality standards and maintain customer satisfaction.
The Benefits of Implementing Quality Control Measures in Manufacturing
Implementing quality control measures in manufacturing provides several benefits. Firstly, it ensures that products meet the established quality standards, which leads to increased customer satisfaction. Secondly, it helps to reduce costs by minimizing waste and improving efficiency. Thirdly, it helps to improve the reputation of the company by ensuring that products are safe and reliable. Fourthly, it helps to increase revenue by making products more appealing to customers. Some of the main benefits of a Quality Controls System include:
- Identifying and correcting defects early: Quality control measures can help identify defects early in the production process before they become major issues. This can prevent the production of defective products that would need to be discarded, saving materials, labor, and time.
- Reducing rework: By ensuring that products meet quality standards, quality control measures can reduce the need for rework. This can save time and materials, and also help to prevent additional defects from being introduced during the rework process.
- Improving efficiency: Quality control measures can help streamline production processes and identify areas for improvement, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. This can help reduce waste by making better use of resources and reducing unnecessary steps in the production process.
- Eliminating unnecessary steps: Quality control measures can help identify unnecessary steps in the production process that do not add value to the final product. By eliminating these steps, manufacturers can reduce waste and increase efficiency.
Common Quality Control Challenges and How to Overcome them
Quality control is an important aspect of the manufacturing process, but it can come with its own set of challenges. Here are some common quality control challenges and how to overcome them:

- Inconsistent raw materials: Inconsistent raw materials can lead to variations in the final product. To overcome this, manufacturers should ensure that they have a reliable supply chain and conduct regular inspections of incoming raw materials to identify any issues.
- Lack of employee training: Employees who are not properly trained may not be able to identify quality control issues. To overcome this challenge, manufacturers should invest in training programs that teach employees how to identify quality control issues and implement corrective actions.
- Lack of quality control measures: Some manufacturers may not have adequate quality control measures in place, which can lead to a high rate of defects. To overcome this, manufacturers should implement a robust quality control system that includes regular inspections, testing, and monitoring.
- Insufficient resources: Lack of resources, including personnel and equipment, can make it difficult to implement effective quality control measures. To overcome this challenge, manufacturers should assess their resource needs and allocate sufficient resources to quality control activities.
- Cultural barriers: Cultural barriers, such as language barriers and differences in work culture, can make it difficult to implement effective quality control measures in a global manufacturing environment. To overcome this, manufacturers should develop clear communication channels and invest in cultural sensitivity training to ensure that all employees can effectively participate in quality control activities.
The Role of Quality Management in Manufacturing
Quality management plays a critical role in manufacturing, and its implementation can significantly impact a company’s success. Quality management is a systematic approach that ensures products are manufactured to meet established quality standards, and customer expectations are exceeded.
The primary role of quality management in manufacturing is to ensure that products meet or exceed customer requirements. Quality management involves the use of quality control techniques to identify and eliminate defects in products. These techniques include statistical process control, Six Sigma, and Total Quality Management (TQM), among others. By implementing quality management, a company can minimize defects, reduce waste, and increase productivity, resulting in cost savings and higher profits.
Besides improving product quality, quality management also helps to ensure that manufacturing processes are optimized. Quality management techniques help to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement in the manufacturing process. By implementing continuous improvement initiatives, companies can improve their manufacturing processes, leading to increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved quality.
Quality management is crucial in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. In many industries, manufacturers are required to meet specific standards and regulations, such as ISO 9001, to operate legally. Quality management helps companies to meet these requirements and maintain compliance, thereby avoiding legal penalties and reputational damage.
The Impact of Quality Control on Customer Satisfaction
Quality control has a significant impact on customer satisfaction in various ways. When a company implements effective quality control measures, it ensures that its products meet the established quality standards. This means that customers receive products that meet their expectations and are of the highest quality. As a result, customers are more likely to be satisfied with their purchase and may even become loyal customers.
In addition, quality control ensures that products are safe and reliable, which is crucial for customer satisfaction. Customers want to be assured that the products they purchase are safe to use and will perform as expected. Unsafe or unreliable products can cause harm to customers, leading to negative reviews, customer complaints, and loss of sales. Therefore, quality control is necessary to minimize the risk of such incidents and enhance customer satisfaction.
Moreover, implementing quality control measures can lead to improved customer service. When a company focuses on delivering high-quality products, it also tends to provide excellent customer service. This can include prompt responses to customer inquiries, efficient handling of complaints, and overall better communication with customers. Such efforts can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, leading to more repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.

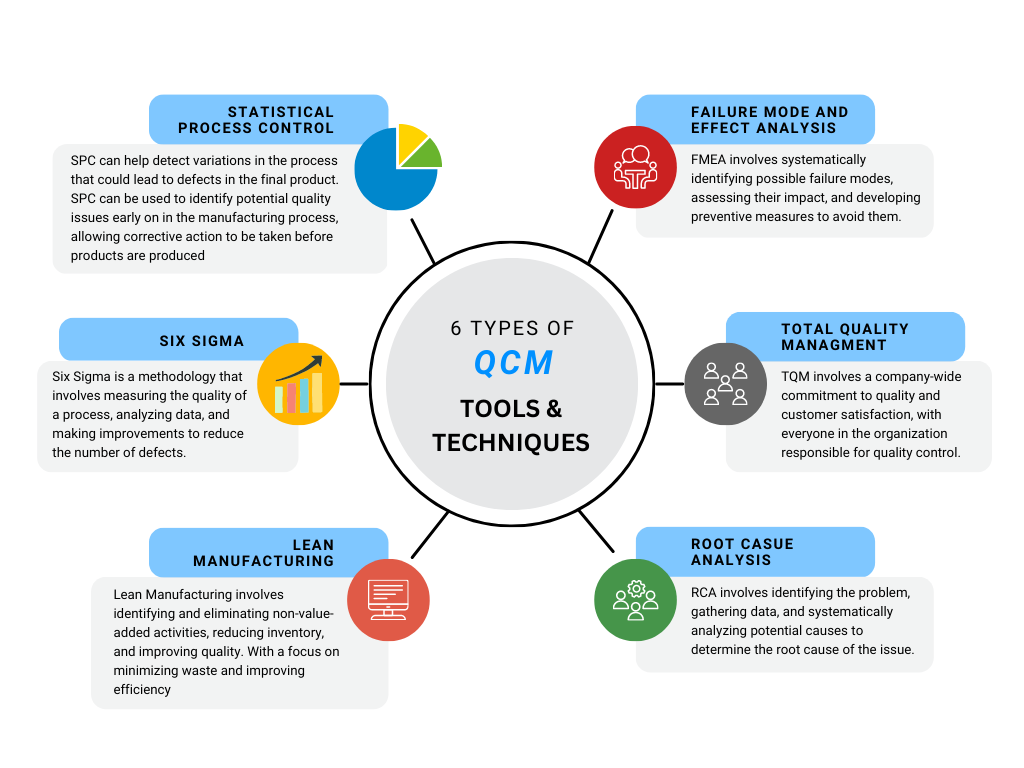
Quality Control Tools and Techniques for Manufacturing
There are various quality control tools and techniques used in manufacturing to ensure that products are manufactured to meet established quality standards. Here are some common quality control tools and techniques for manufacturing:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC involves using statistical methods to monitor and control a manufacturing process. It can help detect variations in the process that could lead to defects in the final product. SPC can be used to identify potential quality issues early on in the manufacturing process, allowing corrective action to be taken before products are produced.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): FMEA is a technique used to identify and analyze potential failure modes of a product or process. It involves systematically identifying possible failure modes, assessing their impact, and developing preventive measures to avoid them.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a methodology that uses statistical analysis to identify and eliminate defects in a process. It involves measuring the quality of a process, analyzing data, and making improvements to reduce the number of defects.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): TQM is a management approach that focuses on the continuous improvement of products and processes. It involves a company-wide commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, with everyone in the organization responsible for quality control.
- Lean Manufacturing: Lean manufacturing is a systematic approach to minimizing waste and improving efficiency in manufacturing. It involves identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities, reducing inventory, and improving quality.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): RCA is a problem-solving technique used to identify the underlying cause of a quality issue. It involves identifying the problem, gathering data, and systematically analyzing potential causes to determine the root cause of the issue.
Quality Control Certifications for Manufacturing
There are several quality control certifications that a manufacturing company can obtain to demonstrate its commitment to producing high-quality products. Here are some of the most common certifications:
- ISO 9001: This is a certification that focuses on quality management. It sets out the requirements for a quality management system, including documentation, process control, and continuous improvement. ISO 9001 is recognized globally and is often a requirement for doing business with certain customers or industries.
- AS9100: This is a certification specifically for the aerospace industry. It includes the requirements of ISO 9001 but also includes additional requirements specific to the aerospace industry, such as the traceability of parts and materials.
- ISO/TS 16949: This is a certification specifically for the automotive industry. It includes the requirements of ISO 9001 but also includes additional requirements specific to the automotive industry, such as customer-specific requirements and product safety.
Quality Control Software for Manufacturing
There are several quality control software solutions that can be used in manufacturing. Here are some of the most popular:

- Statistical Process Control (SPC) Software: SPC software is used to monitor and control quality during the manufacturing process. It provides real-time data on the performance of the process, allowing operators to make adjustments to maintain quality and reduce waste.
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Software: MES software is used to manage and control the entire manufacturing process, from raw material inventory to finished goods. It provides real-time data on the status of each operation, allowing for quick decisions and continuous improvement.
- Enterprise Quality Management System (EQMS) Software: EQMS software is used to manage all aspects of quality control, from audits and inspections to corrective actions and risk management. It provides a centralized platform for quality data, allowing for better analysis and decision-making.
- Document Control Software: Document control software is used to manage all documentation related to quality control, including standard operating procedures (SOPs), work instructions, and quality manuals. It ensures that all employees have access to the most up-to-date information and that changes are properly documented and communicated.
- Supplier Management Software: Supplier management software is used to manage and monitor the quality of raw materials and components supplied by external vendors. It provides a centralized platform for tracking vendor performance and identifying areas for improvement.
- Nonconformance Management Software: Nonconformance management software is used to manage and track deviations from quality standards, including customer complaints, audit findings, and internal quality incidents. It provides a centralized platform for investigating and resolving quality issues.
Quality control software can help to automate quality control processes, monitor production processes, identify quality issues, and track quality metrics. Some popular quality control software solutions include Minitab, QI Macros, and SPC for Excel.

How to Identify areas of Improvement for Quality Control
Identifying areas for improvement is a critical step in implementing effective quality control measures in manufacturing. Here are some ways to identify areas for improvement:
- Conduct regular inspections: Regular inspections of the manufacturing process can help identify areas where quality control measures are not being followed. Inspections can include both visual inspections and testing of samples to ensure that products meet the desired quality standards.
- Analyze customer feedback: Customer feedback can provide valuable insights into areas where improvements can be made. Analyzing customer complaints and feedback can help manufacturers identify common issues and implement corrective actions to prevent future problems.
- Use data analysis: Data analysis can help identify trends and patterns that may be affecting product quality. By analyzing data from various stages of the manufacturing process, manufacturers can identify areas where improvements can be made.
- Conduct employee surveys: Employee surveys can provide valuable feedback on the effectiveness of quality control measures. Surveys can be used to identify areas where employees may need additional training or where processes could be improved.
- Benchmark against industry standards: Benchmarking against industry standards can help identify areas where a manufacturer may be falling behind its competitors. This can help manufacturers identify areas where improvements can be made to stay ahead of the competition.
Conclusion
Quality control is critical for the success of any manufacturing operation. Quality control ensures that products meet the established quality standards, are safe and reliable, and meet the needs of customers. Implementing quality control measures can provide several benefits, including increased customer satisfaction, reduced costs, and increased revenue. There are several best practices for quality control in manufacturing, including defining quality standards, testing products at various stages of production, and having a system in place for continuous improvement. Quality management is critical for ensuring that quality control measures are implemented effectively. Quality control tools and techniques, quality control certifications, and quality control software can all be used to improve quality control in manufacturing. Outsourcing quality control can be a cost-effective solution, but it also increases the risk of quality issues and can result in a loss of control over the production process.

